Contact us: info@tenendo.com
$ git clone git@glab.local:cicd/environment.sh
git: threat model
- external attacker
- authenticated access to an application
- RCE in a docker container
- access to a single server
- access to a developer’s workstation
hardcoded secrets
Not just String pass = "N0OneW1llG3tTh1s";:
- secrets in automated tests and deployment configuration
- secrets in sample front-end code
- hard-coded signatures and HMAC keys
- testing credentials that “bypass” security checks
.git directories
Access to the private Gitlab is not the only way attackers get git access.
- exposure of a
.gitdirectory on - Git repositories used to pull configurations by build agents
.git directories: demo
commits, pulls and branches
- leaked secrets may persist in commit history
- do not only scan the
mainbranch - do not remove secrets by just committing a new version
trufflehog
- the standard for automated secret scanning (especially
git)
trufflehog usage: demo
third-party services + git: real-world example
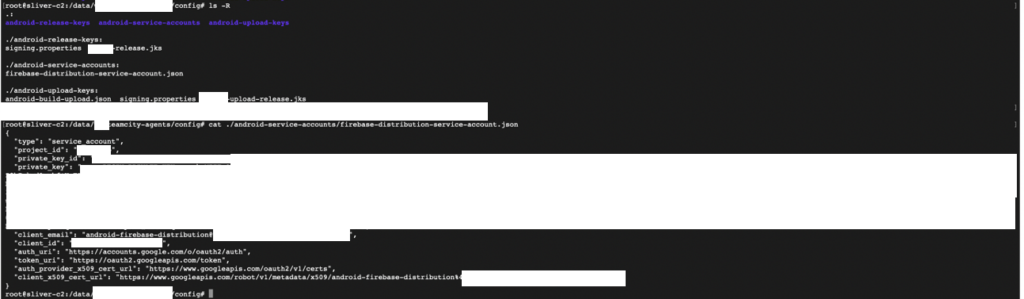
found on Confluence:
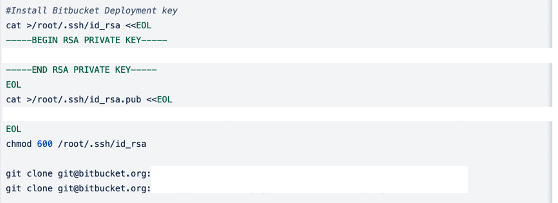
after git clone: