Contact us: info@tenendo.com
Practically all IT company managers and owners eventually come to analyze management processes, evaluate company performance, and identify problem areas. Of course, it is possible and necessary to use IT management standards such as COBIT, ISO for analysis, or apply the experience of successful leaders or consultants.
Let’s apply Henry Ford’s management principles to software development and see how modern development processes align with Ford’s ideas and where the differences lie.
The management principles of Henry Ford, the renowned American industrialist and founder of Ford Motor Company, include the following:
- Principle of specialization and division of labor: Ford introduced the assembly line and divided the production process into a series of specialized tasks. Workers performed narrow and specific operations, which increased productivity and reduced the time required to manufacture automobiles.
- Principle of mass production: Ford advocated for the production of automobiles on a mass scale, which lowered production costs and made cars affordable to a wider audience.
- Principle of standardization: Ford implemented standardized processes and components in automobile production. This improved efficiency, quality, and facilitated repair and maintenance of the vehicles.
- Principle of time management and efficiency: Ford introduced the concept of “flow production” to minimize idle time and optimize the workflow. This led to increased productivity and reduced manufacturing time.
- Principle of cost reduction: Ford aimed to lower the cost of production and sale of automobiles to make them accessible to the general public. He achieved this through process optimization and increased production efficiency.
- Principle of stable wages: Ford implemented the concept of the “five-day workweek” and established stable wages for his workers. This helped increase worker satisfaction, reduce employee turnover, and improve overall work performance.
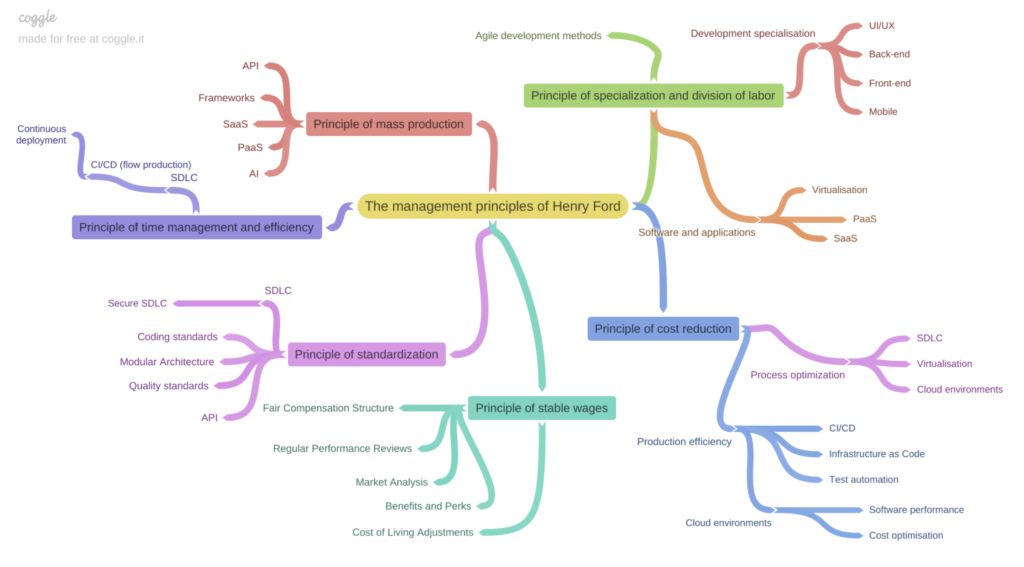
To avoid writing a long text, I have created a mind map:
Of course, this is a simplified representation of how management principles correspond to modern software development practices, but it provides an interesting result:
- Henry Ford’s management principles are applicable to software development.
- Implementing Henry Ford’s principles in software development will lead to an increase in the maturity level of development processes.
- Applying Henry Ford’s principles leads to cost reduction, improved quality, and safety of the end product through Replaceable parts, Perpetual flow, Division of labour, and Reduction of wasted power and effort.
Regarding the end product’s safety, the proliferation of automobiles on the roads led to legislative regulations in road safety and the safety of drivers and passengers. A lot of attention was given to safety in production. Henry Ford actively worked on improving the safety of automobiles and developed standards that became the basis for modern safety systems. He introduced elements such as reinforced body construction, safety glass, anti-theft devices, and braking systems to reduce risks for drivers and passengers.
Let’s turn to statistics.
The size of the software development market compared to the automotive industry. According to the report Global Car & Automobile Manufacturing – Market Size 2005–2028 and Software – Worldwide. The market ratio looks like this:
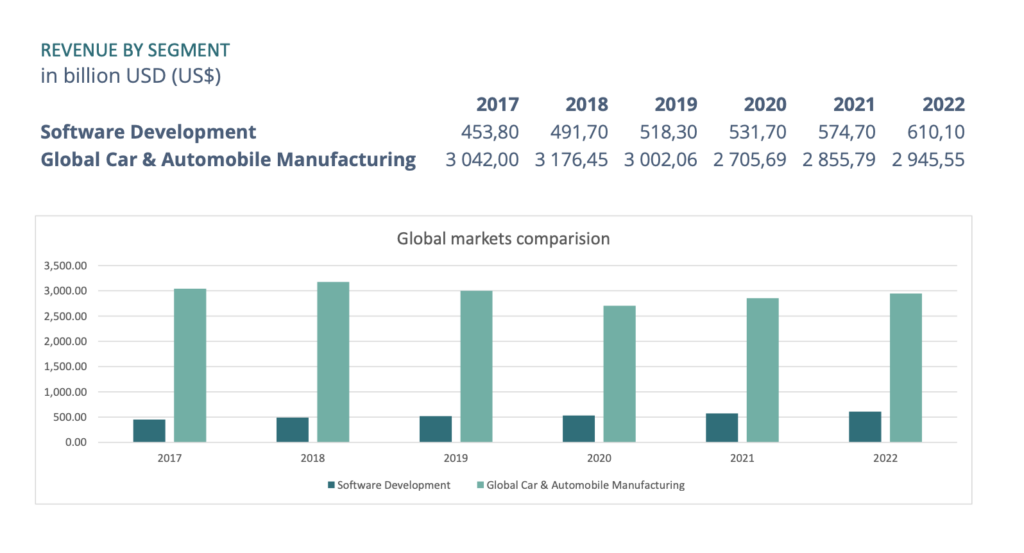
In other words, the Software Development Market is approximately five times smaller than the Automotive Industry Market but shows significantly higher growth in percentage terms: 7.9% compared to 4.5%. There is still room for inefficient processes and inadequate productivity in the software market due to lower competition. Even though the IT industry can still tolerate insufficient quality and inattention to the security of developed products, regulatory control is tightening, particularly regarding the storage and transmission of personal data, similar to what happened in the automotive industry.
In conclusion, I would like to say that despite the latest technologies, approaches, and practices in IT business management, the application of proven old production principles still increases labour productivity, reduces the cost of the final product, and improves its quality and security.
References and Further Reading:
- “My Life and Work” by Henry Ford: This book, written by Henry Ford himself, provides insights into his management philosophies and principles.
- “The Ford Century in Minnesota” by Brian McMahon: This book explores the history of Ford Motor Company and its management practices, including Henry Ford’s contributions.